🔍Mastering Sliding Window Patterns: A Practical Guide for Coding Interviews
Whether you're preparing for FAANG interviews or just want to level up your problem-solving skills, sliding window problems are an essential tool in your algorithmic toolkit. The sliding window technique is all about reducing nested loops and achieving optimal time complexity — often O(n) — by maintaining a subset of data and "sliding" through the input.
In this post, we’ll break down the different types of sliding window problems, how to identify which pattern to use, their time and space complexity, and finally, a curated list of must-solve questions to lock in your understanding.
🔄 What is the Sliding Window Pattern?
At its core, the sliding window pattern is used for problems that deal with contiguous sequences (subarrays or substrings) in arrays or strings. Instead of reprocessing the same elements over and over again, we slide a fixed-size or variable-size window over the data to compute results efficiently.
🧩 Classifying Sliding Window Problems
Sliding window problems generally fall into three main categories:
1. Fixed-Size Sliding Window
Use when: You're asked to find something (sum, average, max, etc.) over every subarray of a fixed size
k.Key insight: Window size remains constant.
Common operations: Add the next element, remove the first element of the previous window.
Example Problems:
Maximum Sum Subarray of Size K
Maximum Average Subarray I
Max/Min in Sliding Window (Deque-based)
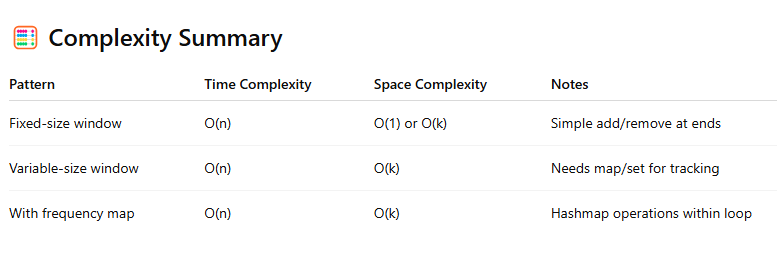
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(1) to O(k), depending on what you're storing
2. Dynamic-Size Sliding Window
Use when: You're looking for the smallest/largest subarray that meets a condition (like a sum or distinct character count).
Key insight: Window size changes based on conditions.
Common operations: Expand the window by moving
right, shrink it by movingleftwhen conditions are met.
Example Problems:
Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
Minimum Size Subarray Sum
Longest Substring with At Most K Distinct Characters
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(k) – usually involves a hashmap to track counts or frequency
3. Sliding Window with Count/Frequency Map
Use when: You need to track frequencies or count elements within the window (often with hashmaps or sets).
Key insight: These problems usually involve strings or distinct counts.
Common operations: Maintain a hashmap or character frequency counter.
Example Problems:
Permutation in String
Anagrams in a String
Longest Repeating Character Replacement
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(k) – for the frequency map
🧠 How to Identify a Sliding Window Problem
Look for these clues in the problem statement:
You're working with contiguous elements in an array or string.
You're asked to find a maximum/minimum/sum/average in a range.
You're scanning for substrings/subarrays that match a condition (like having k distinct characters).
You're trying to avoid nested loops due to time limits.
🧮 Complexity Summary
📝 Must-Solve Sliding Window Problems
Here’s a curated list of problems to master the technique:
✅ Beginner
Maximum Sum Subarray of Size K
First Negative Integer in Every Window of Size K
Maximum Average Subarray I
Find the Length of the Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
✅ Intermediate
Minimum Size Subarray Sum
Longest Substring with At Most K Distinct Characters
Longest Repeating Character Replacement
Permutation in String
✅ Advanced
Sliding Window Maximum (with Deque)
Count Occurrences of Anagrams
Max Consecutive Ones III
Subarrays with K Different Integers
Smallest Window Containing All Characters of Another String (aka Minimum Window Substring)
✨ Pro Tip: Implement each of these using both the brute-force approach and the optimized sliding window method to deeply understand the performance gains.
🧵 Final Thoughts
The sliding window technique is one of the most interview-friendly and performance-critical patterns in competitive programming and real-world systems. Once you recognize the shape of the problem — contiguous range, condition satisfaction, frequency counting — you’ll naturally reach for this pattern.
Master it well, and you’ll slide right past most coding challenges!
📌 Follow Me
If you found this helpful, follow me on Medium for more breakdowns of algorithmic patterns, data structure tricks, and real-world system design!